While conducting research on C#, I discovered the extensive array of frameworks and versions associated with it. It is important to distinguish between these variations and comprehend their usage before we move on to the real project.
C# VS .Net
Starting with C#
C# (pronounced “C sharp”) is a modern, object-oriented programming language developed by Microsoft. It is designed for building a variety of applications on the .NET framework, including desktop applications, web applications, mobile applications, cloud-based services, and more. C# is often used for developing Windows applications and is a key language in the Microsoft technology stack.
C# combines elements of C and C++ with features from other programming languages, such as Java. It provides a strong typing system, automatic memory management through garbage collection, and support for modern programming concepts like object-oriented programming (OOP), generics, and asynchronous programming.
C# is widely used in the software development industry and is the primary language for building applications on the Microsoft .NET platform. It has a large and active developer community, and it is continually evolving with new features and improvements.
.NET
.NET (pronounced “dot net”) is a free, open-source, cross-platform framework developed by Microsoft for building a wide range of applications. It provides a comprehensive set of libraries and runtime for developing and running applications on various platforms, including Windows, macOS, and Linux.
The key components of the .NET framework include:
Common Language Runtime (CLR): The CLR is the execution environment that manages the execution of .NET programs. It provides features such as automatic memory management (garbage collection), exception handling, and just-in-time compilation.
Base Class Library (BCL): The BCL is a collection of reusable classes, interfaces, and value types that provide a standard set of functionality. It includes classes for file I/O, networking, data access, and more.
ASP.NET: A framework for building web applications and services using languages like C# or VB.NET. ASP.NET supports the development of dynamic, data-driven websites and web services.
Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF): A UI framework for building desktop applications with rich user interfaces. It allows developers to create visually appealing and interactive applications.
Windows Forms: Another UI framework for building Windows desktop applications with a more traditional, event-driven programming model.
Entity Framework: An Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) framework that simplifies database access by allowing developers to work with databases using object-oriented concepts.
ASP.NET Core: The cross-platform, high-performance, open-source version of ASP.NET. It is designed to run on Windows, macOS, and Linux and is a key component for building modern, scalable web applications.
.NET supports multiple programming languages, including C#, Visual Basic (VB.NET), F#, and others. Developers can choose the language that best suits their needs while still benefiting from the features and libraries provided by the .NET framework.
Now, we know the different between C# and .Net.
-
C# is just a programming language that used in .Net
-
.Net is a framework to build the application like web application and windows forms, which can be run in different OS environment, including Windows, MacOS and Linux.
.Net framework VS .Net Core Vs .Net
.Net
- Definition: “.NET” is a general term that encompasses the entire ecosystem of Microsoft’s technologies for building and running applications.
- Scope: It includes multiple implementations, such as .NET Framework, .NET Core.
- Cross-Platform: The term “.NET” is used to describe Microsoft’s efforts to make their technology stack cross-platform, supporting development on Windows, macOS, and Linux.
.Net framework
- Definition: “.NET Framework” refers to the original implementation of the .NET platform, initially released in 2002.
- Scope: It is primarily designed for Windows-based applications. It includes technologies like ASP.NET for web applications, Windows Forms for desktop applications, and Windows Presentation Foundation (WPF) for rich user interfaces.
- Compatibility: .NET Framework applications are tied to the Windows operating system.
.Net Core
- Definition: “.NET Core” is a modular, open-source, cross-platform implementation of the .NET platform. Released in 2016.
- Scope: It was developed to address the limitations of the .NET Framework, providing better performance, flexibility, and cross-platform support.
- Cross-Platform: .NET Core supports development on Windows, macOS, and Linux, making it suitable for a broader range of applications.
- Modularity: .NET Core is designed to be more modular, allowing developers to include only the components needed for their applications.
Unified Platform - .Net 5 and Later
- Definition: Starting with .NET 5, Microsoft introduced a unified platform that merges the best features of .NET Core and .NET Framework.
- Cross-Platform: This unified platform supports cross-platform development and is the successor to both .NET Core and .NET Framework.
- Consistency: With the introduction of .NET 5 and later, Microsoft aims to provide a consistent development experience across various application types and platforms.
Here is the picture of release year of different .Net version:
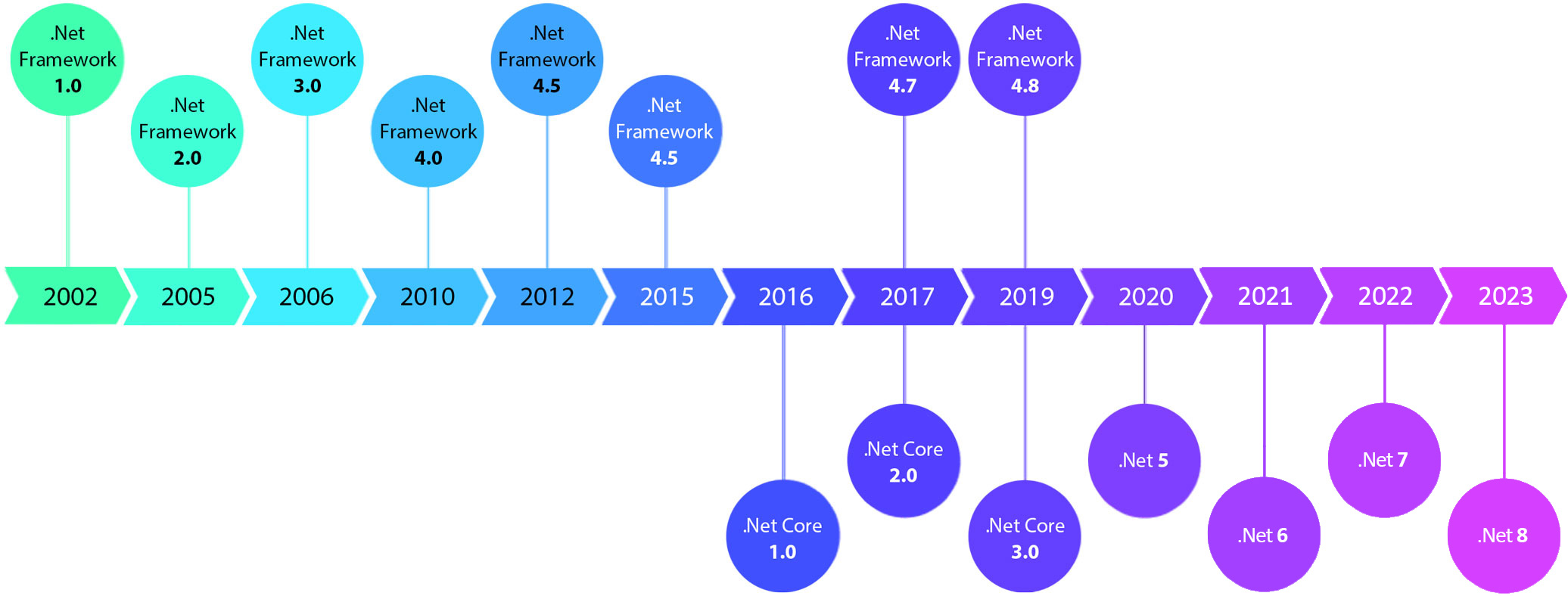
Concludion
From about information, we can say .NET Framework 4.x is a legacy framework, while it continues to be supported, new development efforts are directed towards the unified platform (.NET 5 and later) for broader compatibility.
On the other hand, .Net Core, it is a earlier versions of .Net 5 or later, I think it will be better to use the lastest version of .Net (version 7/8) for a better ongoing support and feature updates.
As I said, I am going build a web application, I will pick .Net 8 and ASP.Net Core 8 on top of it.
Wish me luck.